Case 1 - Right Heavy Tree
Assuming:
- WBT is right-heavy (weight(v.right)>weight(v.left)×3)
- weight(v.right.left)<weight(v.right.right)×2
balance by single counter-clockwise rotation.
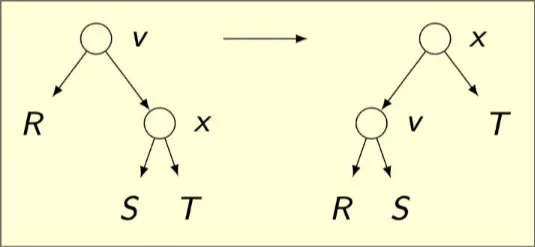
Proof - Uses Diagram Above
- Let r=size(v.left)
- Let s=size(v.right.left)
- Let t=size(v.right.right)
- Suppose s+1<2(t+1)
- Suppose 3(r+1)<s+t+2
- Consider cases:
- Case 1: node added to v.right to cause imbalance
- Suppose before addition, we had a WBT v
- This means, 31∗weight(v.right)≤weight(v.left)≤3∗weight(v.right)
- ⟹31(s+t+1)≤r+1≤3(s+t+1)
- Suppose before addition, we had a WBT x
- This means, 31∗weight(x.right)≤weight(x.left)≤3∗weight(x.right)
- ⟹31(t)≤s+1≤3(t)
- WTS: after addition, and rotation, we have a WBT v and WBT x
- In other words, WTS:
- 31(r+s+2)≤t+1≤3(r+s+2) (WBT x)
- 31(s+1)≤r+1≤3(s+1) (WBT v)
- 3(r+1)<s+t+2=(s+1)+(t+1)<2(t+1)+(t+1)=3(t+1) by 4,5
- ⟹r<t
- Then, r+s+2=(r+1)+(s+1)<(t+1)+(s+1)<(t+1)+2(t+1)=3(t+1) by 4, 10
- t+1≤3(s+1)+1≤3(r+s+2) by 8.1
- r+1<t+1≤3(s+1)+1, therefore r+1≤3(s+1)
- Note that s+1≤s+t+1≤3(r+1)⟹31(s+1)≤r+1
- Thus, we have shown all cases
- Case 2: node removed from v.left to cause imbalance
- Suppose before removal, we had a WBT v
- This means, 31∗weight(v.right)≤weight(v.left)≤3∗weight(v.right)
- ⟹31(s+t+2)≤r+2≤3(s+t+2)
- Suppose before addition, we had a WBT x
- This means, 31∗weight(x.right)≤weight(x.left)≤3∗weight(x.right)
- ⟹31(t+1)≤s+1≤3(t+1)
- WTS: after removal, and rotation, we have a WBT v and WBT x
- In other words, WTS:
- 31(t+1)≤r+s+2≤3(t+1) (WBT x)
- 31(r+1)≤s+1≤3(r+1) (WBT v)
- 3(r+1)<s+t+2=(s+1)+(t+1)<2(t+1)+(t+1)=3(t+1) by 4,5
- ⟹r<t
- r+s+2=(r+1)+(s+1)<(t+1)+(s+1)<(t+1)+2(t+1)=3(t+1) by 4, 11
- t+1≤3(s+1)≤3(r+s+2) by 8.1
- r+1<t+1≤3(s+1) by 8.1, 10
- s+1≤3(r+2)−t−1=3(r+1)+2−t≤3(r+1) when t≥2
Case 2 - Left Heavy Tree
When the WBT is left-heavy - single counter-clockwise rotation.
