A fixed-size Cache that removes the least-used data first.
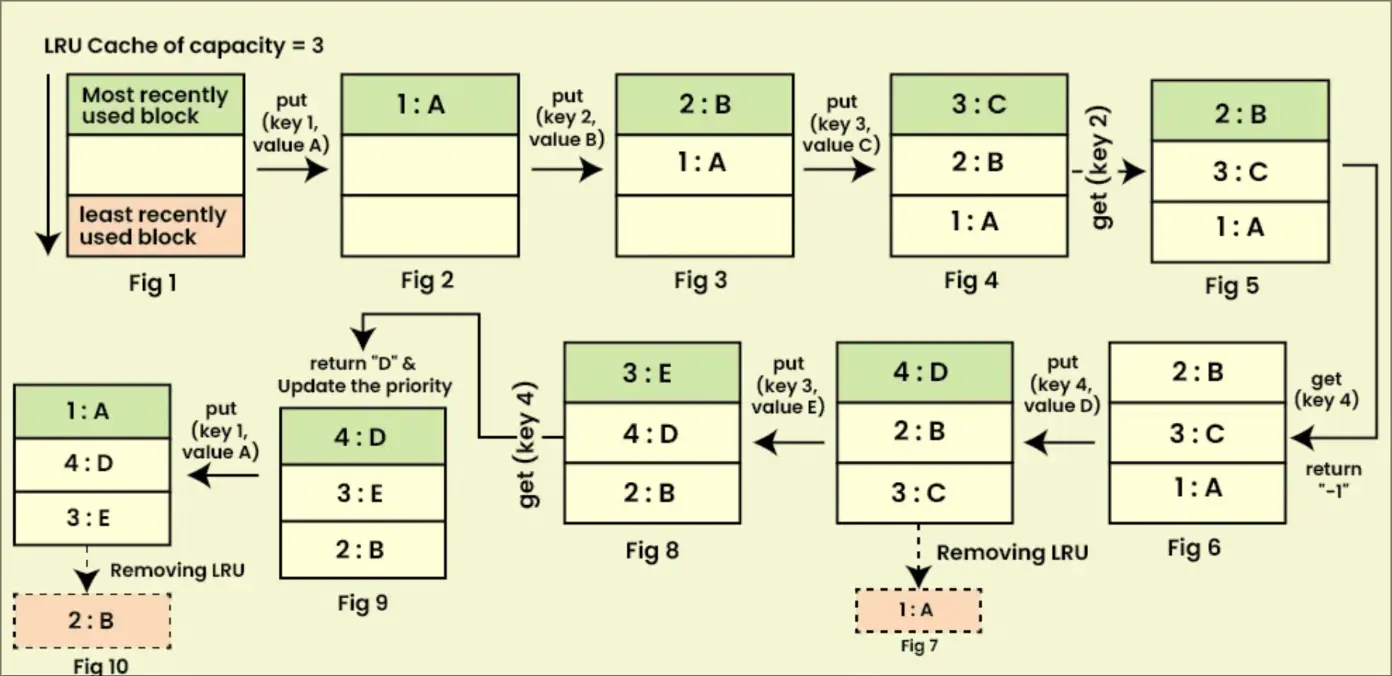
Problem
https://leetcode.com/problems/lru-cache/
Solution
#include "leetcodeutils.hpp"
using namespace std;
struct LRUCacheNode{
int key;
int val;
LRUCacheNode* next;
LRUCacheNode* prev;
LRUCacheNode() : val(0), key(0), next(nullptr), prev(nullptr) {}
LRUCacheNode(int key, int val) : val(val), key(key), next(nullptr), prev(nullptr) {}
};
class LRUCache {
public:
LRUCacheNode* head = nullptr;
LRUCacheNode* tail = head;
map<int, LRUCacheNode*> keymap;
int capacity = 0;
int len = 0;
LRUCache(int capacity) {
this->capacity = capacity;
}
void setmostrecent(LRUCacheNode* val){
if (len == 2){
if (val != tail){
head = tail;
head->prev = nullptr;
head->next = val;
tail = val;
tail->prev = head;
tail->next = nullptr;
}
}
else if (len >= 3){
if (val == head){
LRUCacheNode* a = head->next;
head->next->prev = nullptr;
head->prev = tail;
tail->next = head;
head->next = nullptr;
tail = head;
head = a;
}
else if (val != tail){
val->prev->next = val->next;
val->next->prev = val->prev;
val->next = nullptr;
val->prev = tail;
tail->next = val;
tail = val;
}
}
}
int get(int key) {
// get the value from the keymap
if (keymap.count(key)){
LRUCacheNode* val = keymap[key];
setmostrecent(val);
return val->val;
}
return -1;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if (keymap.count(key)){
keymap[key]->val = value;
setmostrecent(keymap[key]);
}
else{
if(len == capacity){
// get least recently used
int lru = head->key;
keymap.erase(lru);
LRUCacheNode* a = head;
if (len == 1){
head = nullptr;
}
else {
head->next->prev = nullptr;
head = head->next;
}
delete a;
len--;
}
len++;
LRUCacheNode* newnode = new LRUCacheNode(key, value);
newnode->prev = tail;
if (head == nullptr){
head = newnode;
}
else{
tail->next = newnode;
}
tail = newnode;
keymap[key] = newnode;
}
}
};
int main(){
LRUCache* obj = new LRUCache(3);
obj->put(1,1);
obj->put(2,2);
obj->put(3,3);
obj->put(4,4);
cout << obj->get(4) << '\n';
cout << obj->get(3) << '\n';
cout << obj->get(2) << '\n';
cout << obj->get(1) << '\n';
obj->put(5,5);
cout << obj->get(1) << '\n';
cout << obj->get(2) << '\n';
cout << obj->get(3) << '\n';
cout << obj->get(4) << '\n';
cout << obj->get(5) << '\n';
}